Computed Tomography (CT) - Health Library
Health Library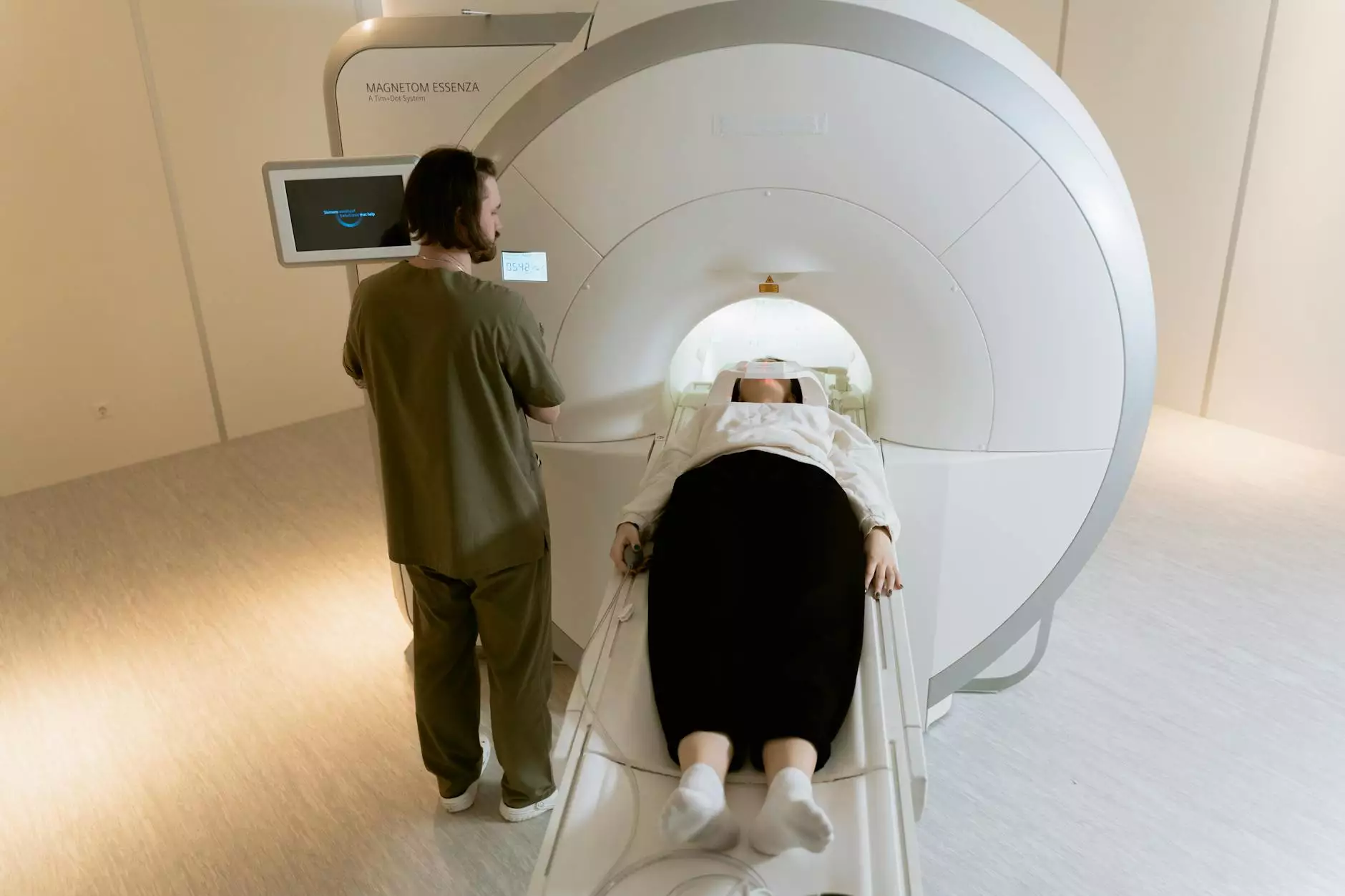
Introduction
Welcome to Furstenberg Michael Dr's Health Library, where we provide comprehensive information about Computed Tomography (CT), a widely used diagnostic imaging technique. Our mission is to educate and inform individuals about the various aspects of CT and its applications in the field of healthcare. As a trusted provider of dental services, Furstenberg Michael Dr believes in the power of knowledge in maintaining optimal oral health.
What is Computed Tomography (CT)?
Computed Tomography, commonly known as CT or CAT scan, is a medical imaging technique that uses X-ray technology and computer processing to generate cross-sectional images of the body. It allows for detailed visualization of internal structures, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions. CT scans provide a more detailed view compared to conventional X-rays, enabling healthcare professionals to identify abnormalities and plan appropriate interventions.
How does Computed Tomography work?
During a CT scan, the patient lies on a table that moves through a circular opening in the CT scanner. X-ray beams are emitted from multiple angles, while detectors measure the amount of radiation passing through the body. The data collected is then processed by a computer to create detailed, three-dimensional images.
Applications of Computed Tomography
1. Medical Diagnostics: CT scans are extensively used for diagnosing a wide range of medical conditions, including but not limited to:
- Cancer detection and staging
- Cardiovascular imaging
- Brain and spinal cord abnormalities
- Lung and chest conditions
- Gastrointestinal disorders
- Orthopedic injuries and fractures
2. Guiding Procedures: CT scans are valuable in guiding various medical procedures, including:
- Biopsies
- Minimally invasive surgeries
- Image-guided radiation therapy
- Catheter and needle placements
Benefits of Computed Tomography
1. Accurate Diagnosis: CT scans provide detailed anatomical information, enabling precise detection and characterization of abnormalities.
2. Non-invasive Procedure: CT scans are generally non-invasive and do not require surgical incisions. They minimize patient discomfort and recovery time compared to invasive procedures.
3. Rapid Imaging: CT scans generate images quickly, allowing for immediate evaluation and timely medical interventions.
4. Pain Management: CT-guided procedures can help alleviate pain by delivering medication directly to the affected area.
Risks and Limitations
1. Radiation Exposure: CT scans involve exposure to ionizing radiation, which, although typically within safe limits, may carry a slight increased risk of cancer development.
2. Contrast Materials: In some cases, contrast agents may be used to enhance the visibility of certain tissues or structures. Allergic reactions or kidney problems can rarely occur as a result.
3. Not Suitable for Everyone: Certain individuals, such as pregnant women and those with severe kidney issues, may need to avoid or modify CT scans to minimize potential risks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Computed Tomography (CT) is a powerful imaging modality that has revolutionized the field of medical diagnostics. It provides detailed and accurate information for the diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring of various medical conditions. However, it's essential to consult with qualified healthcare professionals, like Furstenberg Michael Dr, who specialize in the interpretation of CT scans. Keep yourself informed and make educated decisions to prioritize your health and well-being.